Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians all represent distinct ancient civilizations with unique histories and interactions, notably marked by Roman expansion and rule.
The Romans originate from the city of Rome, which began as a small settlement and grew into a dominant empire. From around 500 BC to 500 AD, Rome expanded its influence across the Mediterranean and beyond. This vast empire included territories once ruled by other civilizations such as Sparta and Egypt.
Egyptians belong to one of the earliest known civilizations, centered around the Nile River in northeastern Africa. Their civilization started around 3100 BC, flourishing under the rule of powerful pharaohs and dynasties for millennia. Despite multiple conquests over centuries, Egypt was eventually conquered by Rome in 30 BC, after which it remained under Roman control for centuries.
Spartans are from Sparta, an influential city-state in ancient Greece. Sparta was known for its military culture and governance as a powerful Greek polis. Founded before 600 BC, it remained significant for centuries until Greece was conquered by Rome. Sparta lost its prominence and was taken by Rome in 146 BC, gradually becoming abandoned due to shifting political and cultural centers.
| Civilization | Origin | Timeline | Roman Conquest |
|---|---|---|---|
| Romans | Rome, Italy | c. 500 BC – 500 AD | Empire expanded over Mediterranean |
| Egyptians | Egypt, Nile River | c. 3100 BC onwards | Conquered by Rome in 30 BC |
| Spartans | Sparta, Greece | Before 600 BC – 146 BC | Conquered by Rome in 146 BC |
The Roman Empire integrated these cultures politically and economically. Egypt became a critical source of grain and wealth for Rome. Sparta’s military traditions influenced Roman martial practices, though as a city-state it lost individual power.
- Romans expanded from a city to a Mediterranean empire lasting about a millennium.
- Egypt, an ancient civilization from 3100 BC, was absorbed by Rome in 30 BC.
- Sparta, a Greek city-state known for military strength, was conquered by Rome in 146 BC and declined thereafter.
Romans, Spartans and Egyptians: A Tale of Three Ancient Powers

Who were the Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians, and how did their stories intertwine? This is a fascinating question that reveals much about ancient history and how these civilizations shaped the world we live in today.
Each of these groups—Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians—represents a unique culture and era. Their histories overlap, clash, and merge in unexpected ways. Let’s unpack their stories and see how these ancient peoples connect.
The Romans: From a Small City to an Empire

The Romans begin simply enough—as residents of Rome, a city founded over 2,700 years ago. What’s striking is how this modest city grew to dominate the entire Mediterranean and beyond.
Starting around 500 BC, Rome evolved from a Republic into one of the most powerful empires in history. Their rule spanned approximately a thousand years, until around 500 AD.
By conquering various regions, including Sparta in Greece and Egypt in Africa, Rome created a vast and diverse empire. Rome’s legacy includes impressive engineering feats, law, language roots, and governance structures that still influence us.
Egyptians: Timeless Civilization Along the Nile

Imagine a civilization thousands of years older than Rome. That’s Egypt, whose history begins around 3100 BC along the fertile banks of the Nile River.
Ancient Egypt is a cornerstone of human civilization, famed for its pyramids, pharaohs, and rich mythology. These kings, or pharaohs, ruled for millennia under many different dynasties.
However, like all great empires, Egypt eventually faced conquest. Rome took control in 30 BC, marking the end of Egyptian independence. The Romans ruled Egypt for centuries, absorbing some of its culture while asserting their authority.
Spartans: The Fierce Warriors of a Greek City-State
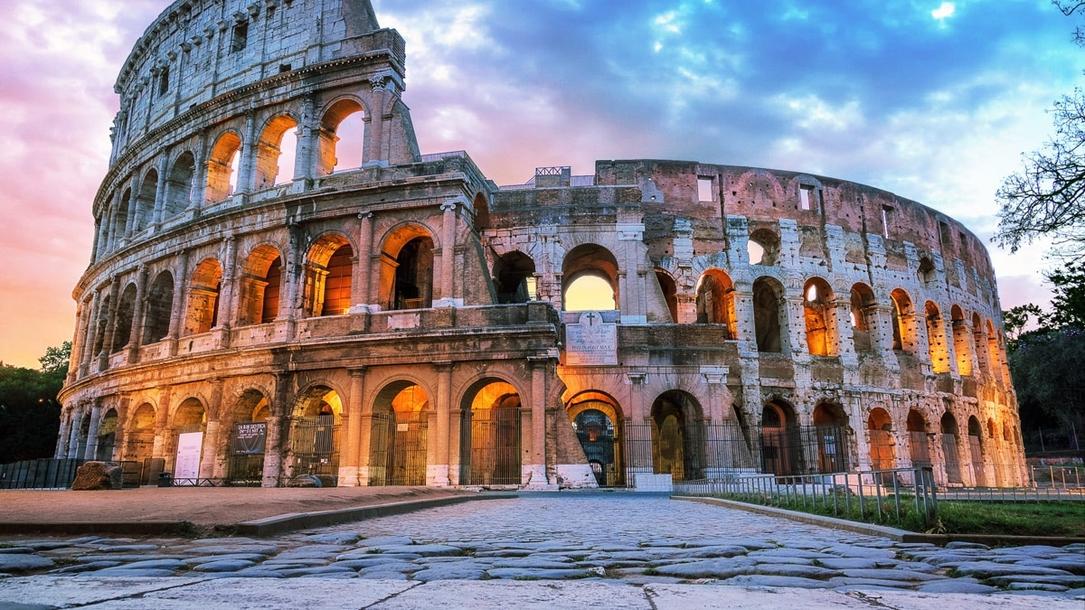

Sparta was quite different. It was a city-state in ancient Greece, renowned for its military discipline and austere lifestyle, founded before 600 BC.
Unlike Egypt’s grandeur and Rome’s sprawling empire, Sparta focused on training warriors and maintaining a rigid social order. Their power peaked in classical Greece but began to fade as Greece fell under Roman dominion.
Rome conquered Sparta in 146 BC. The once-mighty city gradually dwindled and was eventually abandoned.
What Connects These Three?: Empire, Conquest, and Legacy

So what ties Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians together?
Based on history, Rome stands at the center of their overlapping stories. As it expanded, Rome absorbed both Sparta and Egypt.
Rome’s conquest of these lands shows how an empire unites diverse peoples—each with unique traditions, strengths, and destinies—under its umbrella.
The Spartans, originally masters of their own fierce city-state, lost their independence. The Egyptians’ ancient civilization became a Roman province. And yet, aspects of each culture lived on, influencing Roman society and, by extension, Western civilization.
Why Does This Matter Today?

These stories are not just ancient history trivia. They show how cultures interact—through conquest, cooperation, or decline.
Consider how Rome’s legal ideas borrowed from these cultures or how Spartan military concepts inspire modern leadership lessons. Or how Egyptian art and religion continue to fascinate archaeologists and enthusiasts worldwide.
Have you ever wondered what it means for a culture to endure or fade? Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians give us lenses to explore such questions. They teach resilience, the impact of power struggles, and cultural synthesis.
Practical Lessons from Ancient Civilizations
- Adaptability: Rome’s rise shows the power of adapting and expanding while integrating diverse populations.
- Specialization: Sparta’s military focus illustrates how honing a skillset can define a society’s role and legacy.
- Longevity: Egypt’s cultural longevity highlights the importance of strong foundations, traditions, and innovations.
For modern readers, these insights help us understand how societies grow and survive challenges over time.
Final Thoughts: A History Written in Three Acts
The saga of Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians reminds us that history is a living tapestry, woven from diverse threads of power, culture, and time.
Rome’s thousand-year empire didn’t erase the identities of Sparta or Egypt; it transformed and preserved parts of them. Each civilization echoes through today’s world, from architecture to government, from military strategy to cultural heritage.
In the end, these ancient peoples invite us to reflect on our own cultural legacies. How will what we create today be remembered? What connections will future generations see between us, as historians once see between Romans, Spartans, and Egyptians?
“History is not just about the past. It’s about understanding the present and inspiring the future.”
So, next time you think about these ancient civilizations, imagine the conversations they had—or the battles they fought—and appreciate the deep roots of today’s world. Fascinating, isn’t it?